21
Digital Rights
Digital Rights
Content
Young people are online every day, meaning they actively exercise their digital rights while also being vulnerable to their violation. In this playlist, you will learn how to support and protect young people in the digital world.
Digital youth work plays a crucial role in promoting respect for these rights and raising awareness of the associated risks. We will look at the ethical frameworks and practical steps you can take to create a safe digital environment for and with young people. This forms the basis for trust in online relationships.
Key Focus Areas in this Playlist:
- Viewing digital rights as an opportunity within youth work (C3.1).
- Awareness-raising on young people’s digital rights and their risks (C3.2).
- Supporting digital safety and resilience (C3.3).
About the Digital Competence Check
This playlist is directly linked to Competence Area 3 of the Digital Competence Check Digital rights, which is based on the European DYW SNAC Model. The Check covers 5 areas, 14 specific competences, and 38 indicators, helping you to map your starting proficiency level. By following this playlist, you will specifically target and improve the skills identified as areas for development.
This playlist features activities from the platform, all directly connected to this competence area. It is up to you to decide which activities are the most interesting and relevant for your professional development.
Within each activity, you will find four different badges. One badge is specifically intended for the Youth Worker. There are also badges for the Youth Worker's Manager and for Young People, should you wish to involve them in your development. This joint growth path is essential and is rooted in the Digital Systemic Team approach. Evidence shows that digital youth work is best realised when these four roles (Youth Worker, Manager, Young Person) collaborate.
Activities to complete
Complete the following activities, earn badges and you will see your playlist progress updated
Content
This activity invites youth workers, youth work managers, and youth organisations to explore what it takes to build and sustain meaningful digital infrastructure for digital youth work.
The activity draws on insights from the:
- European Commission’s Digital Education Action Plan (see document HERE)
- Youth workers 2.0 - A guide to digital Education for youth workers (see document HERE)
- Ray Digi research report on Exploring successful approaches to digital youth work (see document HERE)
It also relates to global trends in digital transformation and youth work research that identifies infrastructure, funding, and skilled professionals as critical enablers for successful digital youth work. Participants are encouraged to reflect on their organisation’s digital environment, understand the technical and strategic foundations of infrastructure, and co-develop solutions that are inclusive, future-ready, and youth-centred.
By completing this activity, you will:
- Understand the critical role of digital infrastructure in youth work transformation
- Identify the core components, risks, and long-term needs of digital infrastructure
- Recognise how security, accessibility, and sustainability influence digital youth work
- Take practical steps toward planning and advocating for better digital environments
Get inspired
Digital infrastructure has gone from being an innovation to becoming indispensable for education, communication, participation, and employment. With over 90% of jobs requiring digital skills, youth organisations must prepare young people not just to consume technology but to engage with it confidently and critically.
Yet many youth organisations lack the infrastructure — both virtual and physical — to deliver effective digital youth work. Infrastructure includes broadband access, devices, platforms, data security, cloud services, and integration systems. It also involves funding models, maintenance plans, and the people who can use the systems confidently.
The European Commission, alongside youth work researchers, calls for:
- Strategic investment in infrastructure and long-term maintenance
- Better recognition and funding of digital youth work
- Skilled, confident youth workers with both digital soft and hard skills
- Ongoing support for digital ethics, data privacy, and cybersecurity
- Acknowledging that digital activities require just as many (if not more) resources as in-person programming
Download the presentation slides on digital infrastructure for youth work and view the mentimer results about digital infrastructure for youth work.
Infrastructure enables connection, inclusion, innovation, and sustainability — but only if it’s intentionally planned, adequately funded, and continually updated.
Why are we addressing Digital Infrastructure as a key element of Digital Youth work?
In the Ray-Digi Research report “Exploring successful approaches to digital youth work” Digital Infrastructure is recognised as one the three structural pillars identified as key enablers for successful digital youth work, while also pointing out that digital technologies and products are typically not a one-time investment but require long-term maintenance that calls also for digitally skilled and confident youth workers.
The pillars are the following:
- Digital youth work requires rethinking the funding and infrastructure of youth work organisations. Therefore, there is also a need for better recognition of digital youth work.
- Building strong and diverse networks is described as an important structural aspect, also for bridging gaps in the resources of youth work organisations.
- Skilled and confident digital youth workers are a scarce but crucial resource for successful digital youth work. Offering training and support to build both digital soft and hard skills is a need recurrently identified within our interviews.
The Youth workers 2.0 - A Guide to Digital Education for youth workers also recognises Digital Infrastructure as one of the 5 main future challenges in digital education.
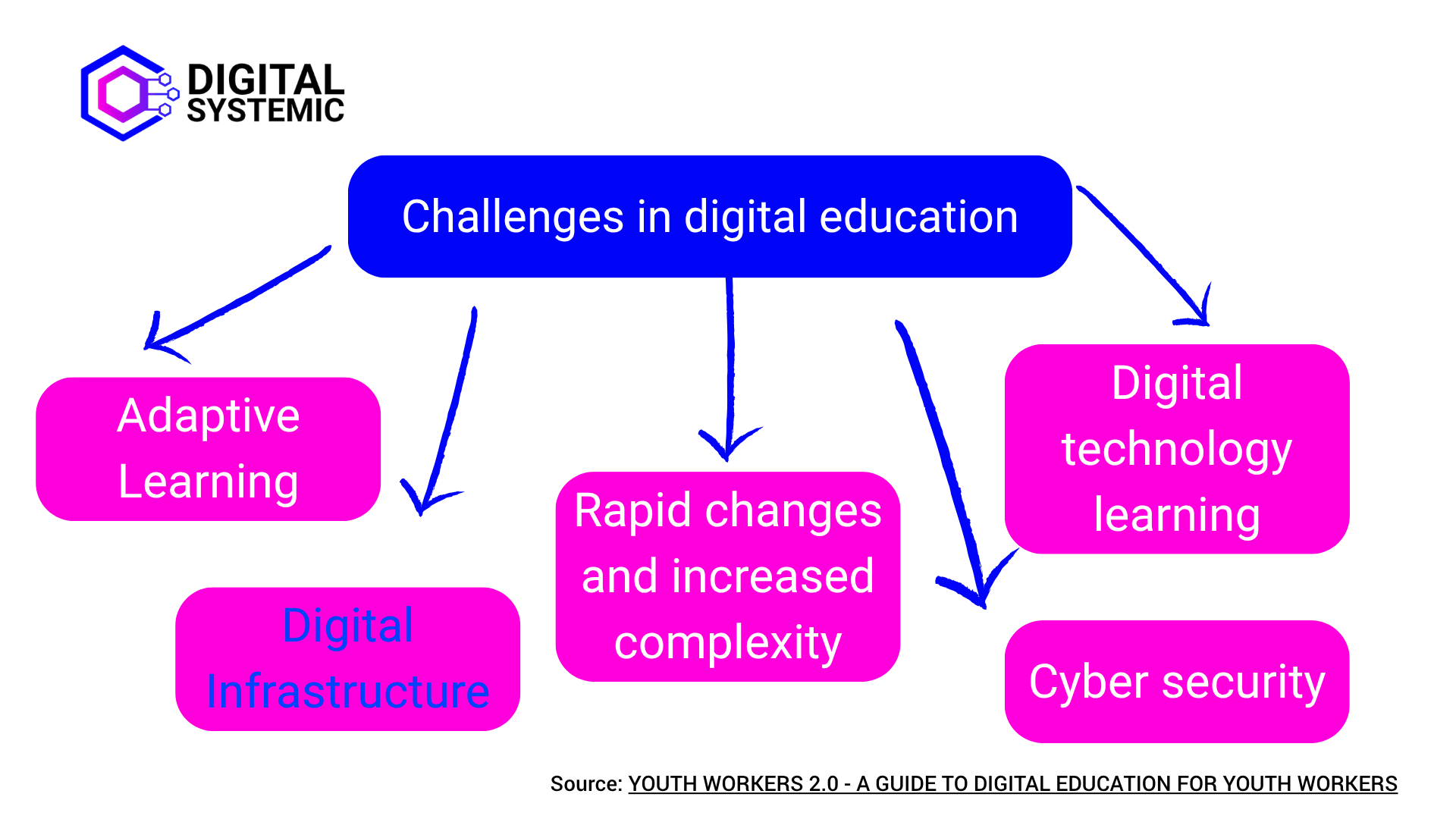
Why does this matter for youth work
As youth work increasingly moves into digital and hybrid spaces, the quality and availability of digital infrastructure directly affect the inclusiveness and effectiveness of your work. However, challenges such as limited broadband access, outdated equipment, or insufficient integration between tools are still common – especially in under-resourced organisations or remote areas.
For youth workers, this means:
- Recognising the importance of reliable infrastructure in designing inclusive and engaging digital youth work activities.
- Collaborating across sectors, including education, technology, and government, to advocate for investment in digital infrastructure where it’s needed most.
- Staying informed about emerging technologies such as cloud services, the Internet of Things (IoT), and M2M (machine-to-machine communication), as these developments will shape how young people interact and learn.
- Planning for the long term, understanding that digital tools are not one-time fixes but evolving systems that require maintenance, updates, and adaptability.
To truly unlock the potential of digital youth work, we need infrastructure that supports:
- Connectivity and inclusion for all young people;
- Adoption of new technologies in safe, sustainable ways;
- Long-term growth of digital literacy and creativity.
Digital infrastructure isn't just a technical issue — it’s a youth equity issue, a learning opportunity, and a shared responsibility. By understanding and engaging with this foundational layer, youth workers can better support the needs and rights of young people in a digital world.
Take action: activities for different roles
Explore these role-specific entry points to build digital infrastructure capacity in your youth work context:
- Youth workers can evaluate their access to digital tools, identify infrastructure barriers faced by young people, and advocate for better digital environments.
- Youth work managers can map digital readiness, review security protocols, and initiate budgeting and investment strategies as well as design long-term infrastructure plans, rethink funding strategies, and build cross-sector partnerships with IT and education providers.
- Young people can be included in infrastructure discussions to ensure tools and environments meet their real needs and reflect their lived digital realities.
Claim open badge recognition
Upon completing this activity, participants can earn badges that recognise:
- Awareness of digital infrastructure as a foundation for digital youth work
- Advocacy for equitable access to digital tools and safe online environments
- Contributions to long-term strategic planning for digital transformation
- Commitment to youth-centred, inclusive digital systems
Who created this resource?
This activity was developed by members of Digital Systemic partnership within the Cities of Learning Network, in response to the insights from the field of digital youth work policy and practice. It builds on the understanding that effective digital youth work depends on more than just tools — it requires infrastructure, skilled professionals, and strategic investment.
Next steps: Use this activity to assess your organisation’s digital infrastructure readiness. Identify areas for investment, security improvements, and youth engagement. Start internal conversations around funding, staff training, and technology maintenance. Connect your efforts with broader national and EU-level digital strategies and contribute to a more equitable, sustainable and secure digital future for all young people.

Resources
Get activity badge
Digital Infrastructure Ally Get this badge
This badge recognises individuals who take initiative in strengthening the digital foundation of youth work. You have explored how digital infrastructure, ethics, and strategy can shape inclusive, responsive, and future-oriented youth engagement.
You have to finish 2 tasks to get the badge
Tasks
Task no.1
Evidence verified by: one activity organiser
Use the "ASSESSMENT TOOL ON DIGITAL CAPACITIES OF YOUTH WORK ORGANISATIONS" to evaluate your organisations digital infrastructure capacities (pages 21 - 22).
Use the provided assessment grid to self-assess the 2 main sub-elements within the "infrastructure" capacity:
- Provision of necessary technologies and competences
- Towards inclusive digital youth work
Task no.2
Evidence verified by: one activity organiser
Find 1-3 additional resources (try local/national, if not use international) that talk about digital infrastructure for digital youth work and answer the following:
- Explore and share how digital technology is transforming youth work (in your country) and what do experts identify as main opportunities and/or risks.
- Find and share examples or experience where infrastructure made or broke a digital youth work initiative. You can use international examples (but please name them and add links) or draw from your own experiences and practice.
- Propose a realistic step that could improve digital readiness in your youth work environment.
Task no.3
Evidence verified by: one activity organiser
Discover Digital Infrastructure in Unlikely Places: Make a quick desk research and find good practice examples of digital infrastructure from outside the youth work field.
Many organisations that do not define themselves as “youth work” actors still create impactful digital opportunities for young people — often without even realizing it. From libraries and makerspaces to tech start-ups, social enterprises, and digital literacy NGOs, there are inspiring initiatives out there that provide access, skills, and support through well-planned digital infrastructure.
Identify 1–2 organisations, projects, or initiatives (local, national, or international) that demonstrate good use of digital infrastructure to support learning, participation, creativity, or inclusion.
These can be schools, tech hubs, online platforms, innovation labs, media education initiatives, etc.
Reflect on what youth work can learn from these examples:
- What aspects of digital infrastructure stand out?
- How do they engage young people?
- Could similar models be adopted in youth work?
Tip: Think beyond hardware. Consider how access, design, partnerships, or sustainability are part of their approach.
Optional: Share links, visuals, or short descriptions of what you found with the community!
Skills
#Good Level. Helps young people to understand the difference between facts, mis/dis-information, and, in general, to critically analyse information.
#Excellent Level. Supportes young people to improve their behaviours in looking for trustworthy sources or running their own online research.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to develop counter-narratives to a case of fake news or disinformation.
#Excellent Level. Helps young people to critically analyse current communication challenges related to the information crisis and the use of synthetic media.
#Fair Level. Sensitise young people on situations when they are not fairly treated in the digitalised world.
#Good Level. Set with young people learning objectives on how to support their digital rights.
#Fair Level. Discusses with young people about the type of digital content they want to produce
#Good Level. Learns to integrate practice-based learning (non-formal learning) and youth participatory approaches in digital youth work practiceer personality.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Good Level. Understands digital youth work in a broad context of social effects and economic interests of digital transformation; applies solid ethical principles to both digital and traditional youth work.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Fair Level. Askes young people to critically assess the practices of the youth work offering.
#Good Level. Sets with young people learning objectives for digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Fair Level. Knows how to support young people to collectively, as a group, gather and reflect on online information (non-formal learning is social knowledge production).
ESCO
#develop a recycling program
ESCO
#checking recycling procedures
ESCO
#advising about pollution prevention
ETS-TR
#Consciously provides space for dialogue and interaction taking into account learners’ values and beliefs and offers space to reflect on them in the educational context
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Good Level. Knows how to organise educational and participatory activities connected to youth’s digital rights, and has been organised several with organisation.
#Good Level. Sets with young people learning objectives for digital youth work.
#Elementary Level. Uses basic digital tools and devices to run some digital youth work activities with young people, based on own intuition
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Constantly assess, together with young people and/or other youth workers on the quality of the digital work and reflects what has been learned; as an intentional process part of the digital youth work strategy.
#Good Level. Plans and implements multiple digital youth work activities, using a diversity of digital tools
#Excellent Level. Shares practices, as a member of a network, which meets regularly and aims at developing digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Good Level. Sets with young people learning objectives for digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Shares practices, as a member of a network, which meets regularly and aims at developing digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Excellent Level. Understands the benefits and risks of gaming and XR, knows how to deal with them and how to guide young people to ethical platforms; when needed, refers young people to specialised support in case of excessive/inappropriate use.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Good Level. Gathers a group of young people to engage in technological activities and agreed about their learning outcomes
#Good Level. Sets together with young people educational aims for their own digital content production
#Good Level. Sets with young people learning objectives for digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Shares practices, as a member of a network, which meets regularly and aims at developing digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Understands the benefits and risks of gaming and XR, knows how to deal with them and how to guide young people to ethical platforms; when needed, refers young people to specialised support in case of excessive/inappropriate use.
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Good Level. Gathers a group of young people to engage in technological activities and agreed about their learning outcomes
#Excellent Level. Understands the benefits and risks of gaming and XR, knows how to deal with them and how to guide young people to ethical platforms; when needed, refers young people to specialised support in case of excessive/inappropriate use.
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Fair Level. Supports young people to learn social skills through participation in digital communities, such as discussion groups, life-style sites, vlogs or gaming.
#Good Level. Plans and implements multiple digital youth work activities, using a diversity of digital tools
#Good Level. Sets with young people learning objectives for digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Runs digital youth work activities that are based on the guidelines of organisation, the ideas of young people, and on the principles set by the national and European organisations.
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Develops an ability to kick-off an innovative spirit in digital youth work activities; intentionally updates competences in the field, and is aware of trends but also policies in the field.
#Excellent Level. Shares practices, as a member of a network, which meets regularly and aims at developing digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Guides a youth group to develop their own initiative on digital rights - using a project, an online study, or managing an exchange program.
#Excellent Level. Knows the key elements of main European digital regulations in the digital field and knows how to ethically apply them in youth work contexts.
#Excellent Level. Confident in using a diversity of digital tools and platforms to support youth work and deliver youth work services. (e.g. advanced technological equipment, digital cameras or software, AI tools)
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Implements a process, designed with organisation, through which assess together with young people the individual and organisational priorities/needs connected to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Confident in using a diversity of digital tools and platforms to support youth work and deliver youth work services. (e.g. advanced technological equipment, digital cameras or software, AI tools)
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Good Level. Ensures that young people with fewer opportunities have participated in digital learning activities, such as thematic events, problem-solving, producing their own content, or vlogs.
#Excellent Level. Shares practices, as a member of a network, which meets regularly and aims at developing digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Fair Level. Supports young people to learn social skills through participation in digital communities, such as discussion groups, life-style sites, vlogs or gaming.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Shares practices, as a member of a network, which meets regularly and aims at developing digital youth work.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Fair Level. Supports young people to learn social skills through participation in digital communities, such as discussion groups, life-style sites, vlogs or gaming.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Excellent Level. Supportes young people to improve their behaviours in looking for trustworthy sources or running their own online research.
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people who independently carries out their content production
#Fair Level. Participates regularly in local, national and/or international e-meetings and e-seminars.
#Awareness-raising on young people’s digital rights and their risks
ESCO
#data privacy
#Good Level. Creates a safe context for digital use and suggested young people to protect themselves from potential cybersecurity threats.
#Fair Level. Knows how to support young people to collectively, as a group, gather and reflect on online information (non-formal learning is social knowledge production).
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Good Level. Learns to integrate practice-based learning (non-formal learning) and youth participatory approaches in digital youth work practiceer personality.
#Fair Level. Discusses with young people about the type of digital content they want to produce
#Fair Level. Advises young people on their basic functional skills, such as critically navigating through a variety of websites and platforms.
#Excellent Level. Runs digital youth work activities that are based on the guidelines of organisation, the ideas of young people, and on the principles set by the national and European organisations.
#Good Level. Runs digital youth work activities based on the guidelines of organisation.
#Excellent Level. Develops an ability to kick-off an innovative spirit in digital youth work activities; intentionally updates competences in the field, and is aware of trends but also policies in the field.
#Good Level. Learns to integrate practice-based learning (non-formal learning) and youth participatory approaches in digital youth work practiceer personality.
#Fair Level. Knows how to easily find online information about young people, and uses in planning digital youth work.
#Good Level. Ensures that young people with fewer opportunities have participated in digital learning activities, such as thematic events, problem-solving, producing their own content, or vlogs.
#Fair Level. Supports young people to learn social skills through participation in digital communities, such as discussion groups, life-style sites, vlogs or gaming.
#Excellent Level. Confident in using a diversity of digital tools and platforms to support youth work and deliver youth work services. (e.g. advanced technological equipment, digital cameras or software, AI tools)
#Fair Level. Discusses with young people about the type of digital content they want to produce
#Fair Level. Exchanges views with young people about their online safety and security.
#Good Level. Understands digital youth work in a broad context of social effects and economic interests of digital transformation; applies solid ethical principles to both digital and traditional youth work.
#Elementary Level. Understands that youth workers and young people should learn together.
#Fair Level. Knows how to support young people to collectively, as a group, gather and reflect on online information (non-formal learning is social knowledge production).
#Good Level. Empowers young people to co-create digital content together with other youth workers/professionals
#Excellent Level. Understands the benefits and risks of gaming and XR, knows how to deal with them and how to guide young people to ethical platforms; when needed, refers young people to specialised support in case of excessive/inappropriate use.
#Good Level. Creates a safe context for digital use and suggested young people to protect themselves from potential cybersecurity threats.
#Excellent Level. Creates different types of digital content and knows how to support others in similar processes (eg. podcasts; videos)
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Good Level. Knows how to organise educational and participatory activities connected to youth’s digital rights, and has been organised several with organisation.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Fair Level. Supports young people to learn social skills through participation in digital communities, such as discussion groups, life-style sites, vlogs or gaming.
#Fair Level. Askes young people to critically assess the practices of the youth work offering.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to create their communities, based on pre-set learning objectives, while reflecting on the results.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people to assess their learnings after running their digital rights activities, and identify new ways of how to address them.
#Excellent Level. Empowers youth groups to use their critical thinking and imagination in order to discuss the ethical implications and find solutions to issues such as profiling, algorithmic filtering or algorithmic bias.
#Good Level. Sets together with young people educational aims for their own digital content production
#Excellent Level. Engages young people on equal footing in the planning, running and evaluation of digital activities; they are an integral part of the strategic approach to digital transformation.
#Good Level. Ensures that young people with fewer opportunities have participated in digital learning activities, such as thematic events, problem-solving, producing their own content, or vlogs.
#Good Level. Gathers a group of young people to engage in technological activities and agreed about their learning outcomes
#Good Level. Learns to integrate practice-based learning (non-formal learning) and youth participatory approaches in digital youth work practiceer personality.
#Excellent Level. Supports young people and other youth workers to set goals for meaningful digital youth work, assess them and reflect jointly on the outcomes.
#Good Level. Plans and implements multiple digital youth work activities, using a diversity of digital tools
#Fair Level. Knows how to support young people to collectively, as a group, gather and reflect on online information (non-formal learning is social knowledge production).
Activities: 20
Started: 52
Completed playlist: 50
Time to complete: 2 days 6 hours 15 minutes
Share:
Organisers
Digital Youth Work Resource Hub
Awero not-for-profit organisation manages this platform and develops it together with leading educational organisations. The European Union's programme Erasmus+ granted co-funding for building the first version of this platform. Contact support@awero.org.
Platform
Change to another language:

